|
|
题目要求
- 定义分子类(Molecule)作为基类,包含集合elements和weight作为其属性,用初始化函数,将elements初始化为空集,weight初始化为None;定义show_weight方法,该方法用print函数打印输出分子量weight;定义show_elements方法,用print函数打印输出元素集合。
- 定义AminoAcid类,==继承Molecule类==,包含composition属性,并初始化为下面的元素字典:{‘C’: 0, ‘H’: 0, ‘O’: 0, ‘N’: 0, ‘S’: 0};定义calc_mw方法,根据根据字典的元素组成,计算其分子量(需要用到每种原子的质量,自己去查),并给继承自父类的weight属性赋值;重载show_weight方法,在其中调用calc_mw方法,计算氨基酸的分子量,再调用父类的show_weight方法,打印输出weight值;重载show_elements方法,用元素字典中的==非零值==的键生成元素集合,再打印输出元素集合。
- 分别定义亮氨酸(Leucine)、异亮氨酸(Isoleucine)、半胱氨酸(Cysteine)类,均继承自AminoAcid类,在初始化方法中,根据这三种氨基酸的元素组成(这个要自己去查),为其继承来的元素字典的各元素对应赋值;定义show_composition方法,打印输出氨基酸的元素字典;在Leucine类中定义is_isoform方法,接受一个氨基酸对象作为参数,根据氨基酸的元素组成,判断是否为当前氨基酸的同分异构体,返回布尔值(True或者False)。
- 分别生成Leucine、Isoleucine、Cysteine类的实例leu、iso、cys,通过该实例,调用其show_weight、show_elements、show_composition等方法,查看当前氨基酸的分子量、元素集合、元素字典;通过leu,调用其is_isoform方法,分别以实例iso和cys为参数,查看各自的返回值,以判定是否同分异构体。
关键点
我们一个一个来看,我把题目的关键点已经加粗了:
- 初始化函数:简单来说就是指的__init __(),也就是构造函数(constructor);
- 空集:这是说的py的一中数据类型——集合。集合(set)是一个无序的不重复元素序列。可以使用大括号 { } 或者 set() 函数创建集合,注意:创建一个空集合必须用 set() 而不是 { },因为 { } 是用来创建一个空字典。
- 继承:这里得用到super().__init__(),如果子类和父类,都写了init方法,那么父类的init方法就会被子类覆盖。想调用父类的init方法需要用super去调用;
- 计算分子量:这里就是原子个数的字典和相对原子质量的字典对应相乘,然后求和。这里用到了map(),一行代码就解决了;
- 非零值:这里是筛选字典中的元素,可以不用循环,用filter()也是一行解决;
- 同分异构体:也就是分子式相同的,在这里也就是elements这个字典类型的数据相同,判断两个字典是否相同,可以直接用==来判断,python已经内置重载了==,极其方便。
代码实现
注释比较详细,下面就是代码了~
class Molecule:
'''
Molecule类
elements初始化为空集,weight初始化为 None;
show_weight方法,该方法用print函数打印输出分子量 weight;
定义show_elements方法,用print函数打印输出元素集合。
'''
def __init__(self):
# 用set()来初始化空集
self.elements = set()
self.weight = None
def show_weight(self):
print(self.weight)
def show_elements(self):
print(self.elements)
class AminoAcid(Molecule):
'''
AminoAcid类(继承Molecule类)
composition:初始化的元素字典
Molecular_mass:相对原子质量
'''
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.composition = {'C': 0, 'H': 0, 'O': 0, 'N': 0, 'S': 0}
self.Molecular_mass = {'C': 12, 'H': 1, 'O': 16, 'N': 14, 'S': 32}
''' 另一种写法:直接在calc_mw()中给self.weight赋值,后面直接调用show_weight()即可
def calc_mw(self):
self.weight = sum(map(lambda x, y: x * y, self.composition.values(), self.Molecular_mass.values()))'''
def calc_mw(self):
# 对应元素的个数和相对原子质量相乘并求和
return sum(map(lambda x, y: x * y, self.composition.values(), self.Molecular_mass.values()))
def show_weight(self):
# 重新定义show_weight(),也就是更新了一下分子质量并且打印,
self.weight = self.calc_mw()
print(self.calc_mw())
def show_elements(self):
# 将原子个数大于0的原子重新组合成名为 elements 的集合
self.elements = set(dict(filter(lambda item: item[1] > 0, self.composition.items())))
print(self.elements)
# print(type(self.elements))
class Leucine(AminoAcid):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.composition = {'C': 6, 'H': 13, 'O': 2, 'N': 1, 'S': 0}
def show_composition(self):
# 与 elements类似,数据类型是字典
self.elements = dict(filter(lambda item: item[1] > 0, self.composition.items()))
print(self.elements)
# print(type(self.elements))
def is_isoform(self, another):
# python内置重载了"==",可以实现字典相等与否的判断
return True if self.elements == another.elements else False
class Isoleucine(AminoAcid):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.composition = {'C': 6, 'H': 13, 'O': 2, 'N': 1, 'S': 0}
def show_composition(self):
self.elements = dict(filter(lambda item: item[1] > 0, self.composition.items()))
print(self.elements)
class Cysteine(AminoAcid):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.composition = {'C': 3, 'H': 7, 'O': 2, 'N': 1, 'S': 1}
def show_composition(self):
self.elements = dict(filter(lambda item: item[1] > 0, self.composition.items()))
print(self.elements)
leu = Leucine()
iso = Isoleucine()
cys = Cysteine()
print("leu:")
leu.show_weight()
leu.show_elements()
leu.show_composition()
print("iso:")
iso.show_weight()
iso.show_elements()
iso.show_composition()
print("cys:")
cys.show_weight()
cys.show_elements()
cys.show_composition()
print("leu & iso: {}".format(leu.is_isoform(iso)))
print("leu & cys: {}".format(leu.is_isoform(cys)))下面是运行结果:
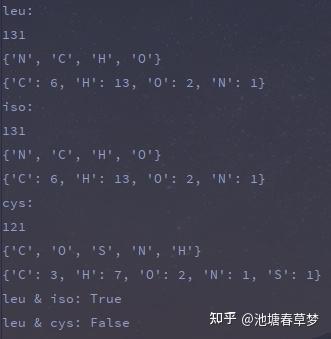
运行结果 |
|